算法课的相关笔记。Modular arithmetic 、Primality testing、Cryptography(RSA)、Hashing。
教材:
Algorithms (Umesh Vazirani, Christos H. Papadimitriou )
脑图由豆包生成
Big O notation

Chapter1: Algorithms with numbers
Multiplication and division
Div:1
2
3
4
5
6if x = 0: return (q, r) = (0, 0)
(q, r) = divide(⌊x/2⌋, y)
q = 2 · q, r = 2 · r
if x is odd: r = r + 1
if r ≥ y: r = r − y, q = q + 1
return (q, r)
Modular arithmetic
The algorithm will halt after at most n recursive calls, and during each call it multiplies n -bit numbers, for a total running time of
Extended Euclid algorithm
Eculid:1
2
3
4
5Euclid(a, b)
// Input: two integers a and b with a ≥b ≥0
// Output: gcd(a, b)
1. if b = 0 then return a
2. return Euclid(b, a mod b)
- The correctness is by
mod y , y ) for all - The running time is
Extended Euclid:1
2
3
4
5
6
7ExtendedEuclid(a, b)
// Input: two integers a and b with a ≥b ≥0
// Output: integers x, y, d such that d = gcd(a, b) and ax + by = d
1. if b = 0 then return (1, 0, a)
2. (x', y', d) = ExtendedEuclid(b, a mod b)
3. (x, y) = (y', x' − ⌊a/b⌋y')
4. return (x, y, d)
- The correctness is by
mod y , y ) for all - The running time is
Modular inverse
We say x is the multiplicative inverse of a modulo N if
inverse不一定存在,且最多存在一个。
Theorem (Modular Division Theorem):
For any a mod N ,a has a multiplicative inverse modulo N if and only if it is relatively prime to N (i.e..
Primality testing
Fermat’s little theorem
proof:
构建非零整数模 p 的集合 . 当集合 S 中的元素都乘以a(mod p)时,得到的结果集合与原集合\S是相同的,只是元素顺序发生了变化(即这些数是 S 的一个排列)。基于此,将两个集合的元素分别相乘,可得,由于(p - 1)!与p 互质(因为p 是质数),两边同时除以(p - 1)!,就可以得到。
局限:
- 费马小定理的逆命题不成立,即如果,则 p 不一定是质数。
,但是合数。
Carmichael numbers:
There are composite numbers N such that for every (a<N) relatively prime to N (Carmichael numbers are composite),
Example: 561 = 3 · 11 · 17
An algorithm for testing primality with low error probability:1
2
3
4
5
6
7primality2(N)
// Input: positive integer N
// Output: yes/no
1. Pick positive integers a1, a2, . . . , ak < N at random
2. if $a_{i}^{N-1}$ ≡ 1 (mod N) for all i = 1, 2, . . . , k then return yes
3. else return no.
Pr(primality2 returns yes when N is prime) = 1
Pr(primality2 returns yes when N is not prime) ≤
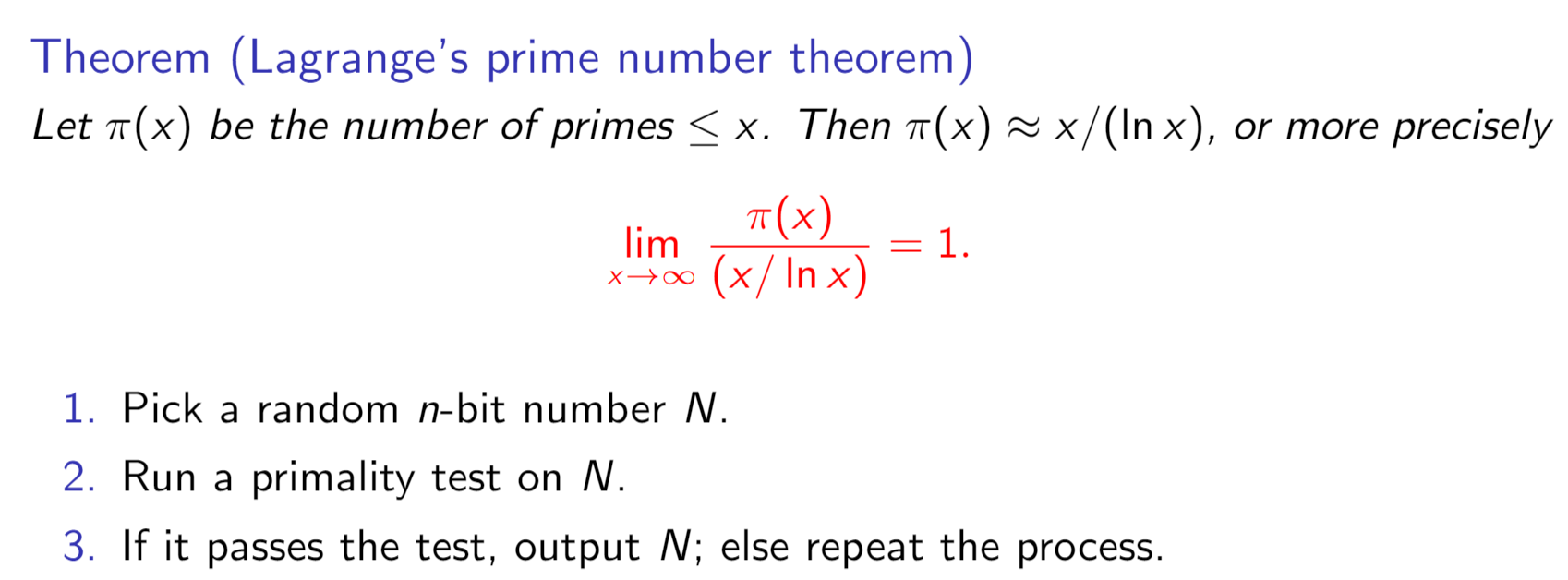
If the randomly chosen N is truly prime, which happens with probability at least 1/n, then it will certainly pass the test. So on each iteration, this procedure has at least a 1/n chance of halting. Therefore on average it will halt within O(n) rounds.
Cryptography
RSA
RSA加密算法的步骤如下:
密钥生成
- 选择两个大质数p和q
- 计算n = p × q
- 计算φ(n) = (p-1)(q-1)
- 选择一个与φ(n)互质的整数e作为公钥
- 计算私钥d,使得d × e ≡ 1 (mod φ(n))
加密过程
- 公钥: (n, e)
- 明文消息m
- 加密: c =
解密过程
- 私钥: (n, d)
- 密文c
- 解密: m =
示例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14# 一个简单的RSA实现示例
p = 61
q = 53
n = p * q # n = 3233
φn = (p-1) * (q-1) # φn = 3120
e = 17 # 选择e与φn互质
# 计算d: 17d ≡ 1 (mod 3120)
d = 2753 # 私钥
# 加密消息m = 123
c = 123^{17} mod 3233 = 855 # 密文
# 解密
m = 855^{2753} mod 3233 = 123 # 恢复明文
pf:
If x →
To (2), we first observe that e is invertible module (p − 1)(q − 1) because it is relatively prime to this number. It remains to show:
Since ed ≡ 1 mod (p − 1)(q − 1), we can write ed = 1 + k(p − 1)(q − 1)
since
Since p and q are primes, this expression must be divisible by N = pq.
Hashing
example: IP address
We can define a function h from IP addresses to a number mod n as follows:
Fix any four numbers mod (n=257) , say 87, 23, 125, and 4.
Now map the IP address to mod 257.
In general for any and define
Consider any pair of distinct IP addresses and . If the coefficients are chosen uniformly at random from , then

