Overview
Process is a program in execution.
Basics
Concept
- sequential not parallel
Process vs Program
- Program becomes process when an executable file is loaded into memory
| 维度 | 程序(Program) | 进程(Process) |
|---|---|---|
| 定义 | 存储在辅助存储(如硬盘)中的静态指令集合,是被动实体 | 程序执行时的动态实例,是主动运行的实体 |
| 属性 | 仅包含指令和数据的静态描述 | 包含程序计数器、内存状态、寄存器值等运行时状态 |
| 生命周期 | 长期存在(除非被删除) | 临时存在(从创建到终止) |
| 资源需求 | 无需占用系统资源(仅存储时占用磁盘空间) | 需要CPU时间、内存、I/O设备等资源 |
| 控制结构 | 无控制块 | 拥有进程控制块(PCB),记录运行状态和资源分配 |
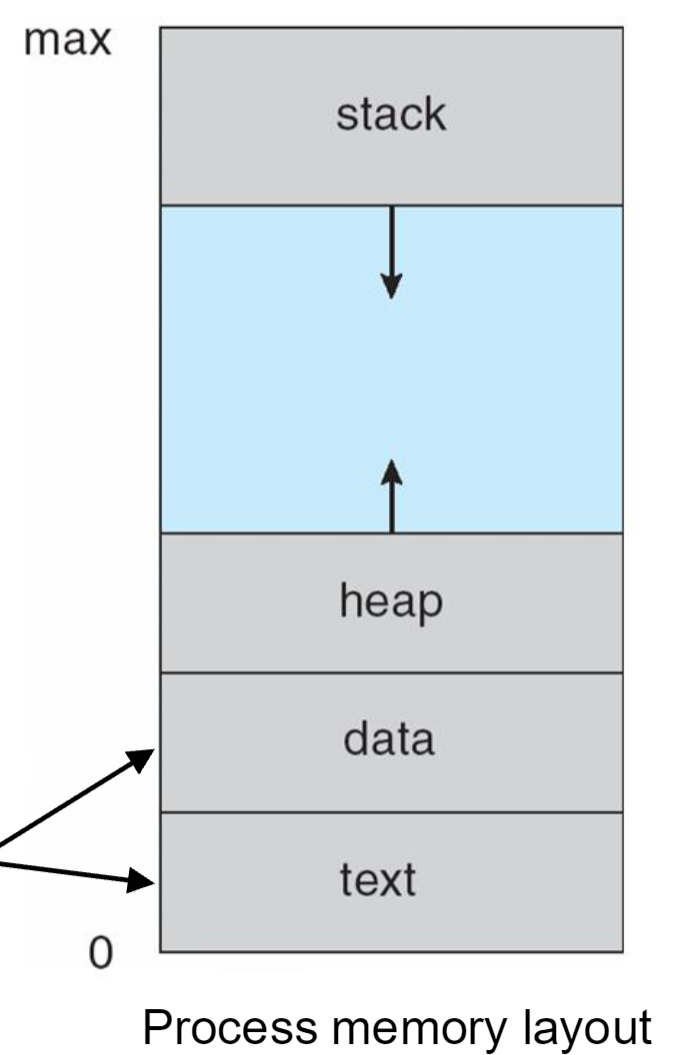
Memory
- Stack: local variables, function parameters, return address
- Heap: dynamic memory allocation
- Data: global variables fixed
- Text: code fixed
Current Process are recorded in PCB
- Program Counter
- Processor Registers
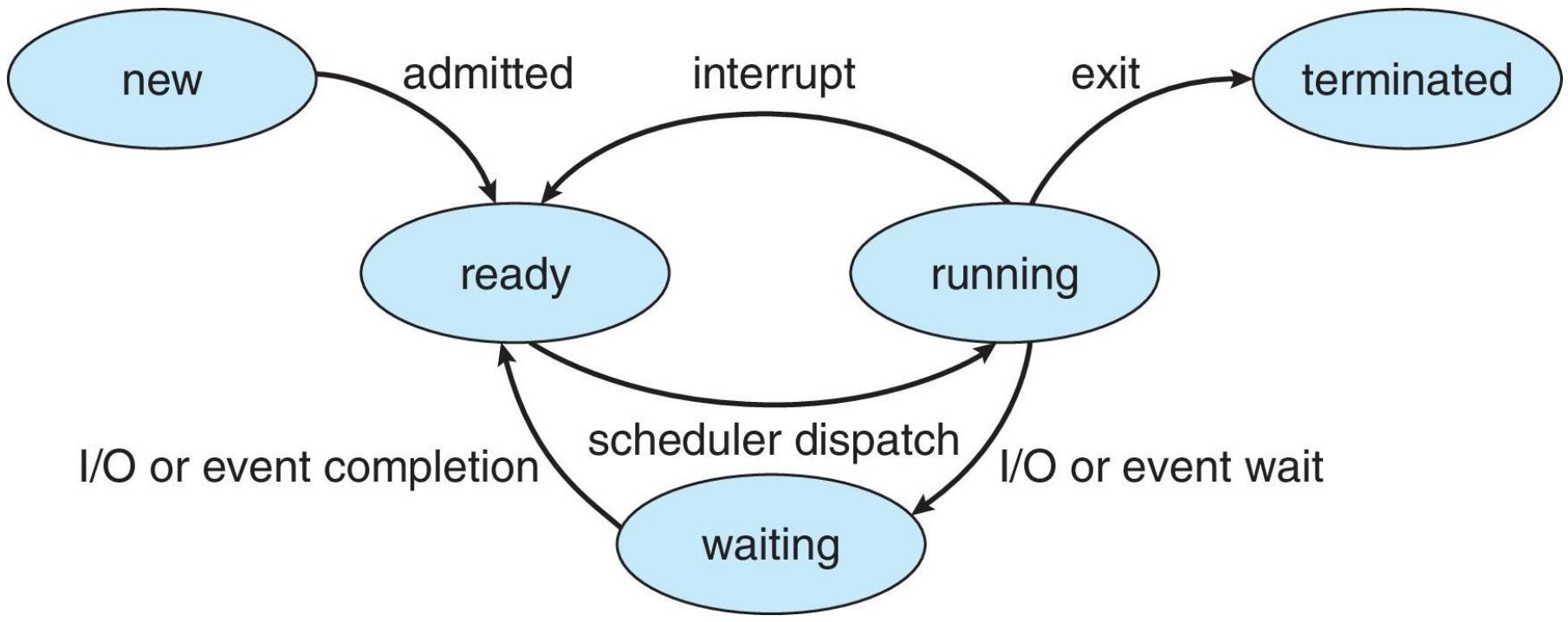
Process State
- New: The process is being created
- Ready: The process is waiting to be assigned to a processor
- Running: Instructions are being executed
- Waiting: The process is waiting for some event to occur
- Terminated: The process has finished execution
Process Control Block (PCB)
- Process ID
- Process State
- Program Counter
- CPU Registers
- Process Memory Address
- CPU Scheduling Information
- Accounting Information
- I/O Status Information
Scheduling
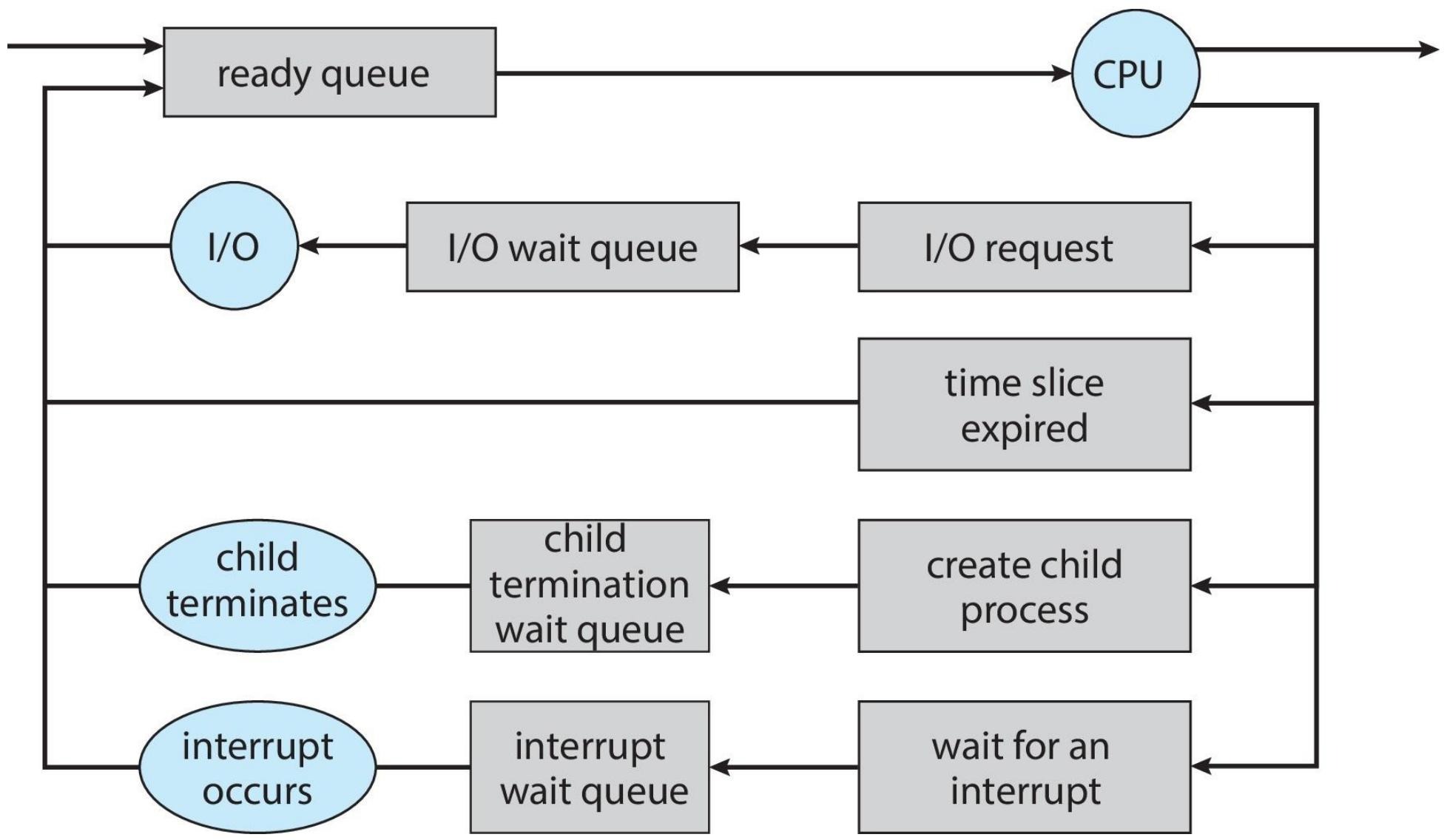
Process scheduler selects among available processes for next execution on CPU core.
Maintains scheduling queues of processes:
- Ready queue
- Wait queue
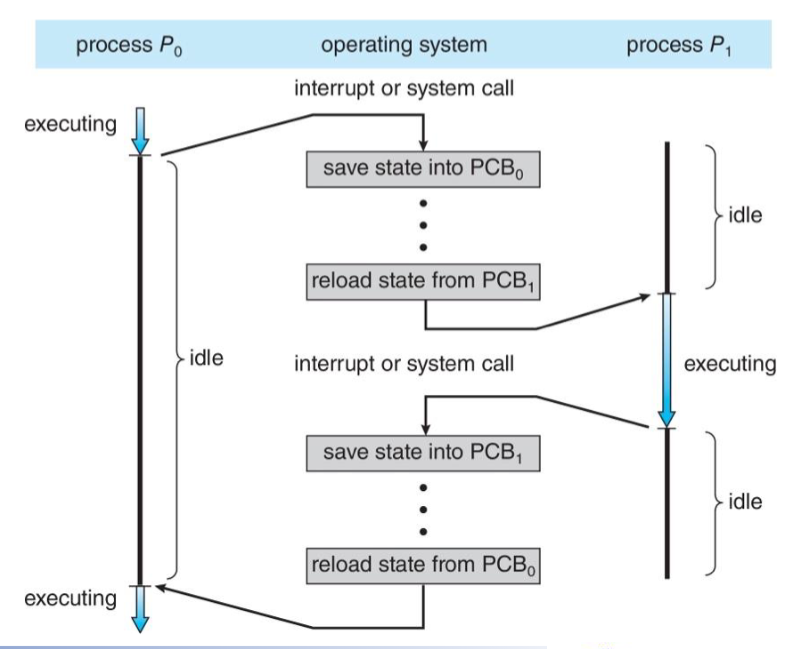
Context switch
- Save current process state
- Load next process state
- Switch to the next process
切换时间属于纯开销(overhead),受硬件影响(寄存器数量)
Scheduler
- Long-term scheduler: 进程筛选(哪些进程进入ready queue),慢速
- Short-term scheduler: CPU调度(运行哪个进程),实现并发,快速
Operations
Process Creation
- 父进程创造子进程(树状结构)
- resource sharing
- execution : 并发/父进程等待子进程终止
- address space: 复制fork() / 加载新程序exec()
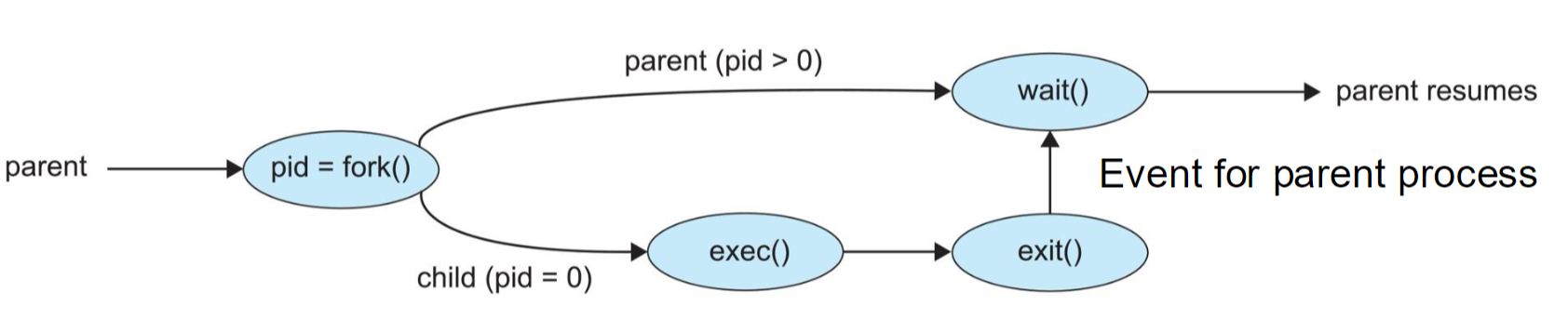
进程执行fork(), 子进程会从父进程上次执行语句的下一句开始执行。
eg. 三次fork(), 产生8个进程。
Process Termination
- 子进程终止(exit)
- 父进程回收子进程的资源(via wait())
- abort() 级联终止(Cascading termination)
- 孤儿进程(orphan process):父进程终止,子进程继续运行
- 僵尸进程(zombie process):子进程终止,父进程未回收资源
- 孤儿进程和僵尸进程的解决方案:init进程(pid=1)
Interprocess Communication
| 维度 | 共享内存 | 消息传递 |
|---|---|---|
| 核心 | 内存共享,直接读写 | 消息中转,间接通信 |
| 速度 | 快 | 慢 |
| 复杂度 | 高(需同步) | 低(系统抽象) |
| 适用场景 | 单机高频、紧耦合 | 分布式、松耦合 |
| 同步机制 | 显式同步(如互斥锁、信号量) | 隐式同步(如消息队列) |
| 可扩展性 | 差(受限于内存大小) | 好(分布式扩展) |
Shared Memory
Producer process produces information that is consumed by a consumer process
- Unbounded buffer
- Bounded buffer
Message Passing
Direct Communication
显式命名
通信链路:需显式建立和关闭
示例:
进程 A 调用send(B, “Hello”),直接向进程 B 发送消息。
进程 B 通过receive(A, msg)接收来自 A 的消息。
Indirect Communication
Messages are directed to and received from mailboxes (also referred to as ports)
- Each mailbox has a unique ID
- Processes can communicate only if they share a mailbox
Synchronous (同步)
- Blocking
- 发送方直到接收方准备好,一直阻塞,直到消息被接收
- 接收方直到消息接收,一直阻塞
- Non-blocking
Pipe
管道是一种半双工的通信通道,允许一个进程的输出直接作为另一个进程的输入。
本质是借助内核缓冲区实现的伪文件。
Require parent-child relationship.
Ordinary Pipe / Anonymous Pipe
数据只能从管道的写入端流向读取端,具有单向性。
需要通信进程之间存在父子关系且在同一台机器上。
Named Pipe
Communication is bidirectional.
No parent-child relationship
Communication in Client-Server Systems
Socket
IP 地址用于唯一标识网络中的设备,而端口号则用于区分同一设备上的不同网络服务,定位具体进程。
Create a socket:
- Server side
- bind()
- listen()
- accept()
- read() / write()
- close()
- Client side
- connect()
- read() / write()
- close()
每一个连接都具有唯一的套接字对,进程间只能交换简单字节流,无法相互转发有结构的数据包。
Remote Procedure Call
RPC 是一种分布式计算的通信协议,允许一个进程调用另一个进程中的函数。
RPC 通过网络通信,将本地函数调用转换为远程函数调用。
- 本地调用:
- 调用本地函数
- 返回结果

