Overview
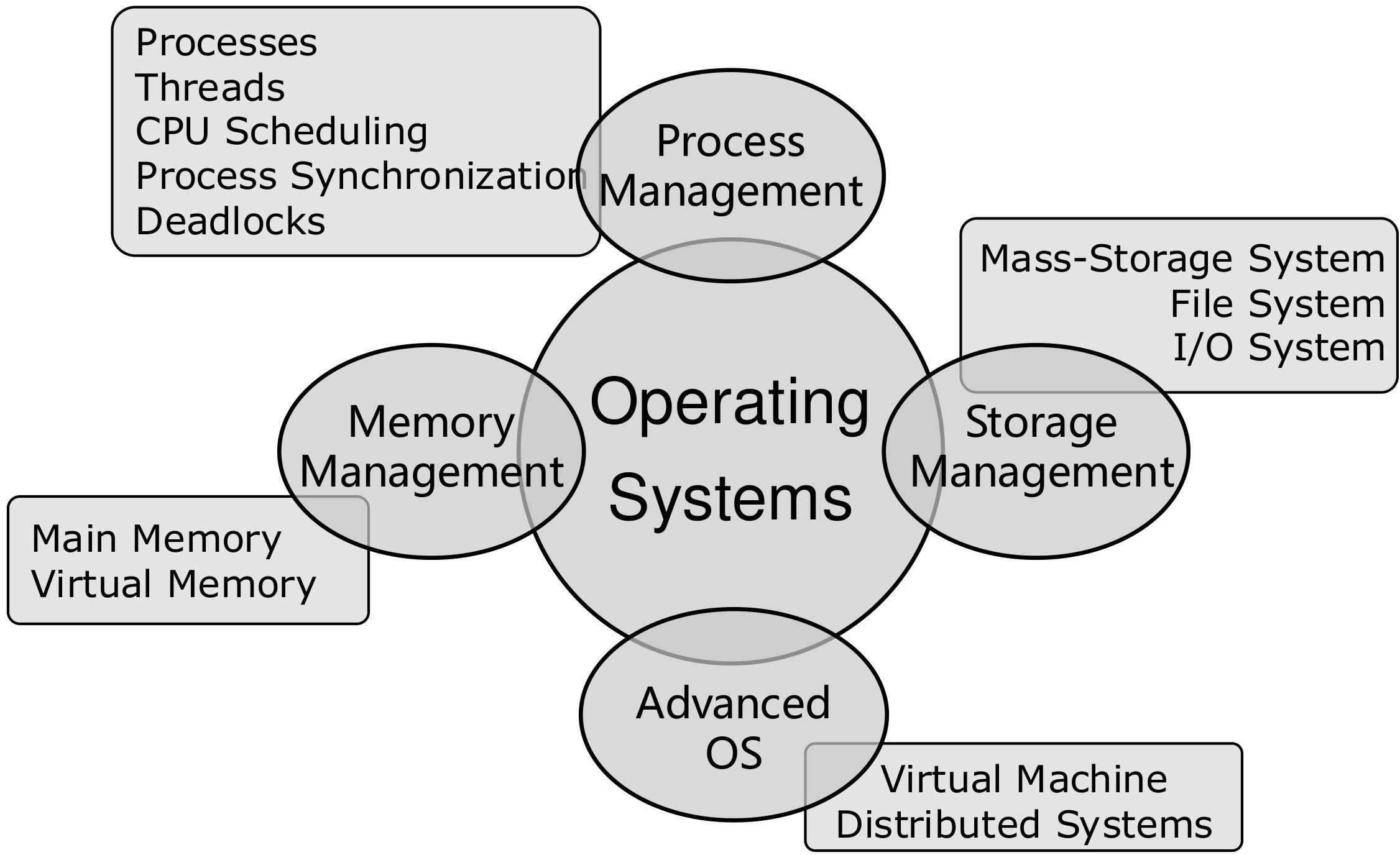
Operating systems provide an environment for program executions and services to programs/users
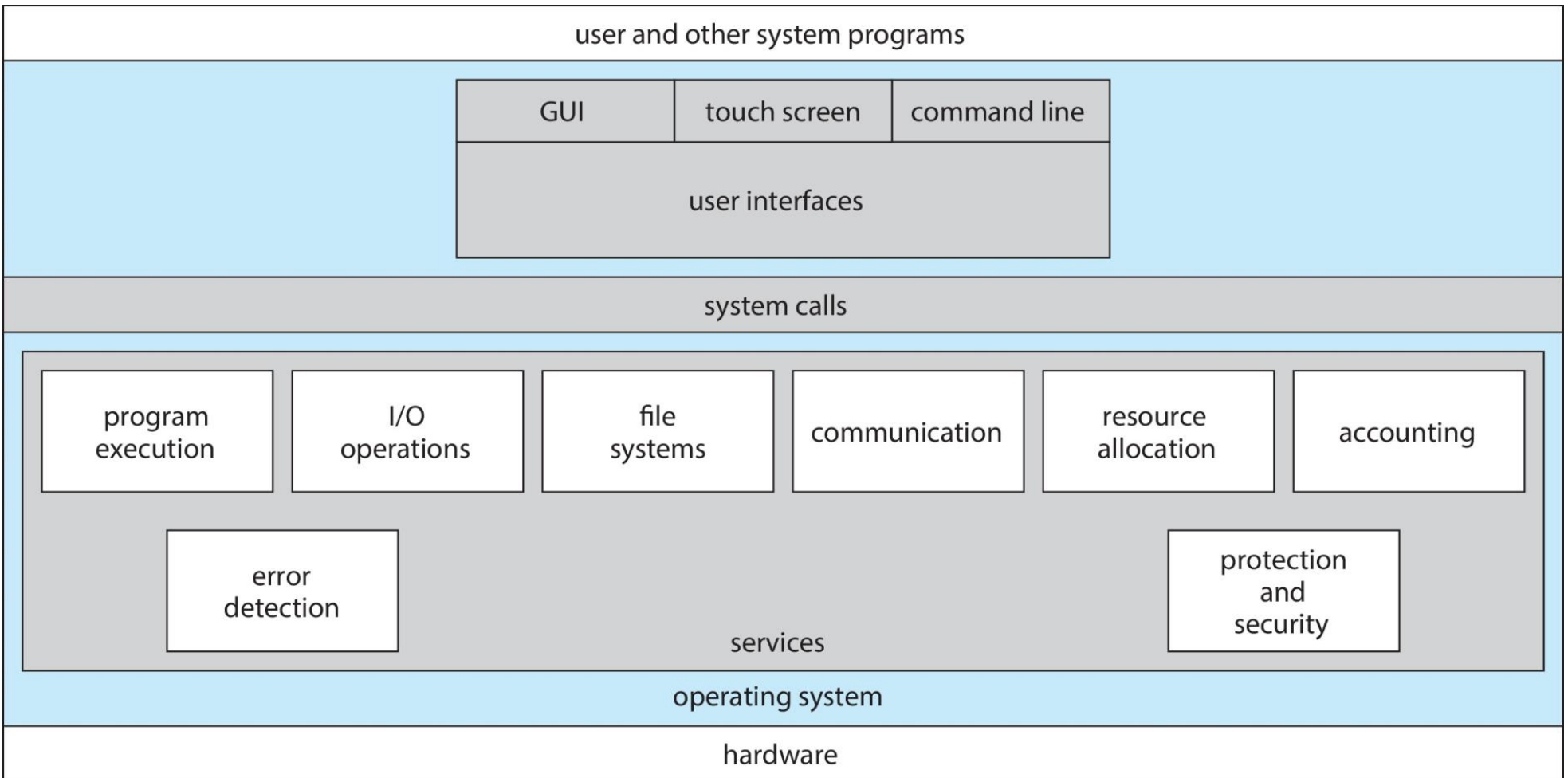
Functions
User Interface
Shell: A computer program that exposes an OS’s services to a human user or other programs. OS shells use either a command-line interface (CLI) or a graphical user interface (GUI)
An interpreter
CLI
Shell:
- Built-in commands: The interpreter contains the code to execute the command.
- 直接执行 eg.
cd
- 直接执行 eg.
- System program commands: The command is a program name.
- 查找系统文件执行 eg.
ls
- 查找系统文件执行 eg.
System Calls
Mode
- User
- Kernel
转换:系统调用,中断,异常
API
System calls are mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface (API) rather than direct system call use.
性质:
- 易用:无需了解底层实现,直接调用
- 可移植:API具有跨平台兼容性
- 安全:直接调用与内核交互
Parameter Passing
- 寄存器:快,少
- 内存表
- 栈
The last two methods do not limit the number or length of parameters being passed 性能损耗
Types
Type 1: Process control
- Control the current process: end, abort, execute, load……
- Control a different process
- Allocate memory and release memory
- Debugger
- Locks for managing access to shared data between processes
Type 2: File management
Type 3: Device management
Type 4: Information maintenance
Type 5: Communications
- message passing model 内核中转,离散
- shared-memory model 共享物理内存
Type 6: Protection
System Services
In computer hierarchy, system services are higher than system calls.
System services use system calls to interact with the OS kernel
Programs
- System Programs:Login program, shell, window manager
- Application Programs:Email, web browsers, gaming software, word processors
Why Applications are Operating System Specific:
Reason: Each operating system provides its own unique system calls
eg. file format
Services
- File management
- Status information
- Some systems implement a registry (注册表) - used to store and retrieve configuration information
- File modification
- Programming-language support
- Program loading and execution
- Communications
- Background Services
- Known as services, subsystems, daemons
Operating System Structures
- Simple Structure – MS-DOS
- Monolithic (单体)Structure – Original UNIX
- Layered Approach
- Microkernel System Structure - Mach
- Hybrid Systems - windows, macOS, Android
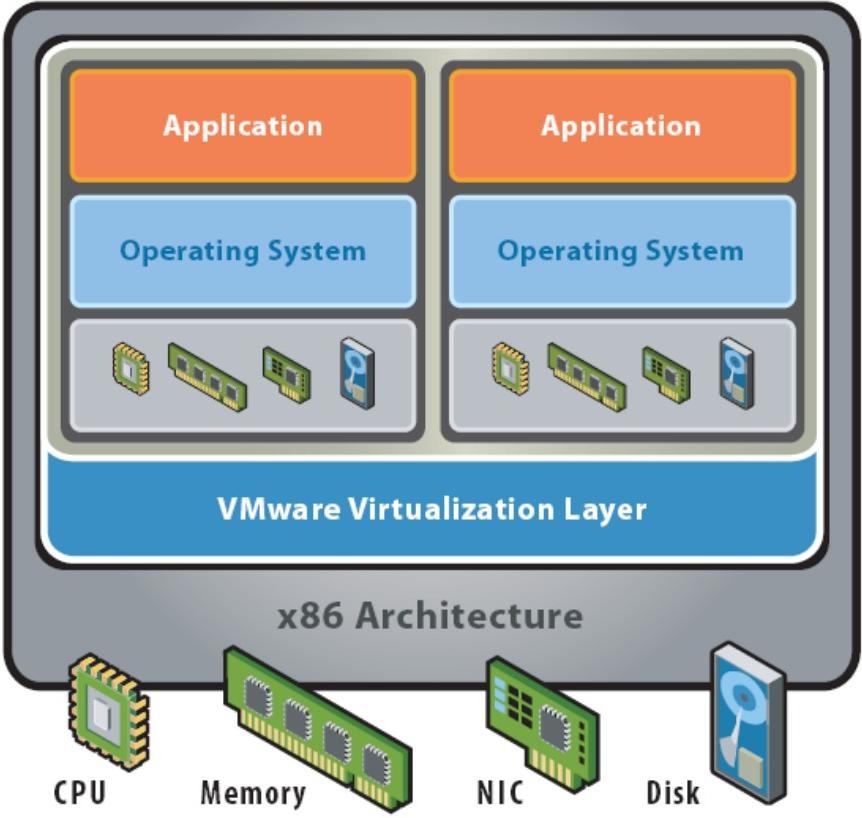
Virtual Machines
Summary